What are Insulin and Glucagon?
Insulin is a hormone made by our pancreas that allows the body to use sugar from carbohydrates in the food that you eat for energy or for future use. Insulin acts like a key to allow glucose into the cells.
Glucagon, on the other hand, is a peptide hormone that is produced by alpha cells of the pancreas. Its purpose is to raise the concentration of glucose and fatty acids in our bloodstream. It is considered to be the main catabolic hormone of the human body.
When the glucose level in the blood falls, cells in the pancreas secrete glucagon. Glucagon instructs the liver to convert glycogen into glucose. Therefore, making glucose more available in the bloodstream. It is from here that insulin attaches to the insulin receptors in cells to make sure they can absorb glucose.
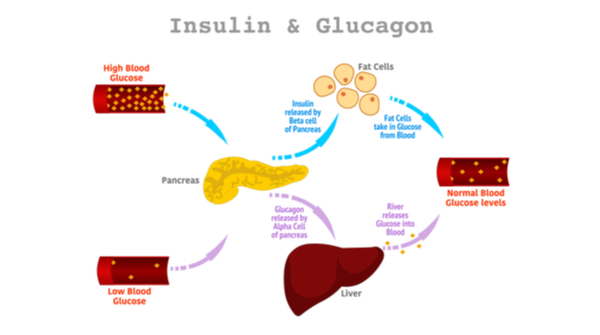
Function Of Insulin And Glucagon On Blood Glucagon Levels
The pancreas secretes insulin and glucagon, both of which play a vital role in regulating sugar levels in the blood.
The two hormones work together and if even one does not function right then it can cause an imbalance in blood sugar levels.
In simple words, when sugar is high, the pancreas secretes more insulin, and when blood sugar levels drop, they release glucagon to bring it back to normal. When it comes to managing diabetes, the normal functioning of both becomes extremely crucial.
Signs of blood sugar imbalance:
The ideal blood sugar ranges are as follows:
- Before breakfast: Less than 100 mg/dl for a person without diabetes and 70-130 mg/dl for a person with diabetes.
- Two hours after meals: Less than 140 mg/dl for a person without diabetes and less than 180 mg/dl for a person who has diabetes.
When sugar levels get out of hand, our body starts giving us signs. Watch out for:
- Dizziness
- Frequent Thirst
- Fatigue
- Numbness
- Swelling in hands and feet
- Poor vision
- Frequent infections
Talk to your medical advisor:
Knowing how your body works can help you stay fit and keep problems at bay. Insulin and glucagon are two critical hormones for diabetes management. It helps to understand how these hormones function so you can work to avoid diabetes and its related health complications.
Read More: Yoga for Diabetes: Best Asanas/Poses With Steps For You
Consult BeatO’s health coach for free and control your diabetes. Download the BeatO app!
Check your blood sugar level with Beato Glucometer today.





